With over 26 billion devices worldwide, technology security is more important now than ever. The best thing you can do to protect yourself and your information is to be educated and stay diligent with your security practices. With technology constantly updating and changing, it’s important to stay informed to keep attackers at bay.
When it comes to stealing your information, attackers will try many different routes, whether it’s an email, text, or phone call. Oftentimes, attackers make these seem urgent, whether it’s an email from the CEO of your company, or a text message regarding your banking activity – they want to create a sense of urgency which makes you reactionary, acting question. If you don’t know how to properly identify these attacks, you may accidentally give attackers access to your information or allow them to install malware* on your device.
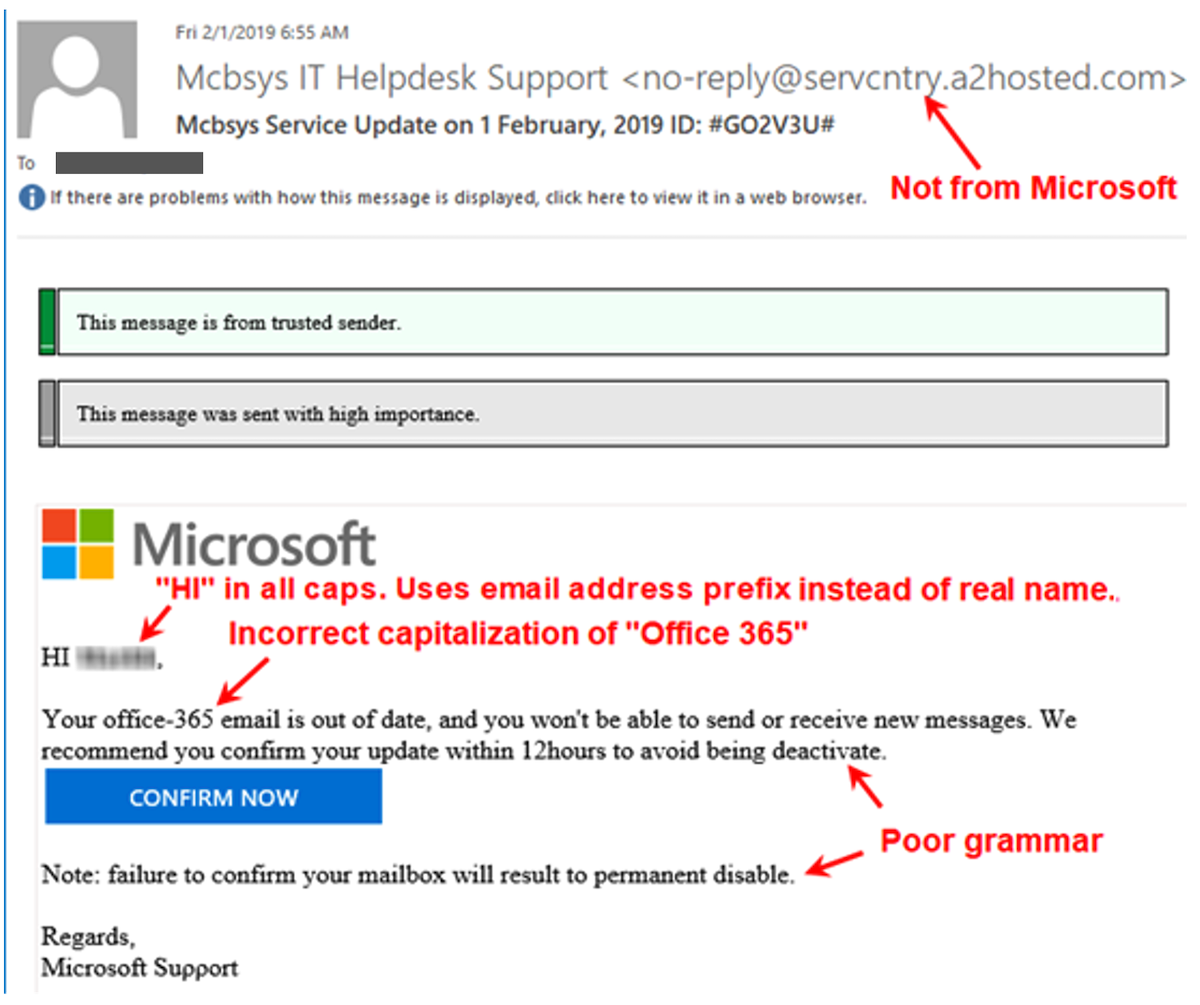
Below is an example of a phishing* email, including a few things to watch out for. If you think you might have received a phishing email, don’t open any attachments, or click any links. It’s extremely important to review emails before you open or respond to them. Check for things such as poor grammar, see if the email address matches the senders name (or a variation thereof), and check for any suspicious links.
Another way to keep your devices safe is by choosing complex passwords or pass phrases and avoid using the same password for different websites. Creating a complicated password, makes it more difficult for the attacker to guess. Changing your password every 90 days also makes it more difficult for attackers. If the attacker can guess an often-used password once, they’ll have access to those accounts. Consider a password manager like LastPass or 1Password which help you create more secure passwords for use across your devices.
If you think that you may have received a phishing email or may be compromised, it’s best to check with your IT department and follow their instructions. ###
*Phising – A technique for attempting to acquire sensitive data, such as bank account numbers, through a fraudulent solicitation in email or on a web site, in which the perpetrator masquerades as a legitimate business or reputable person.
*Malware – Hardware, firmware, or software that is intentionally included or inserted in a system for a harmful purpose.